Guidelines for Single Organization RBAC Management
Managing role-based access control (RBAC) within a single organization requires a clear understanding of role assignments and permissions. This guide outlines best practices for assigning roles effectively, ensuring security, and planning for future growth. If you are considering expanding your account or are on a trial version, it is crucial to understand how roles function at both the global and organization levels.
Refer to Roles and Permissions Management for details about creating roles.
Understanding Role Assignments
When managing roles within a single organization, it is crucial to distinguish between global roles and organization-specific roles, as this impacts future access control.
Global Roles
- You can only assign Account and Global roles from the Setup & Configuration pages:
- Roles and Permissions page: Add to Role
- Users page: Add User or click the email to open the Edit User page
- These roles apply across all current and future organizations added to the account.
- A role assigned at the global level is inherited by any future organizations. Example: When a global Full Administrator role is assigned to a user, that user will have these permissions for all new organizations added to the account.
- When you assign a global role to a user from the organization-level Settings > Users page, that role is then limited to that specific organization.
Organization-Level Roles
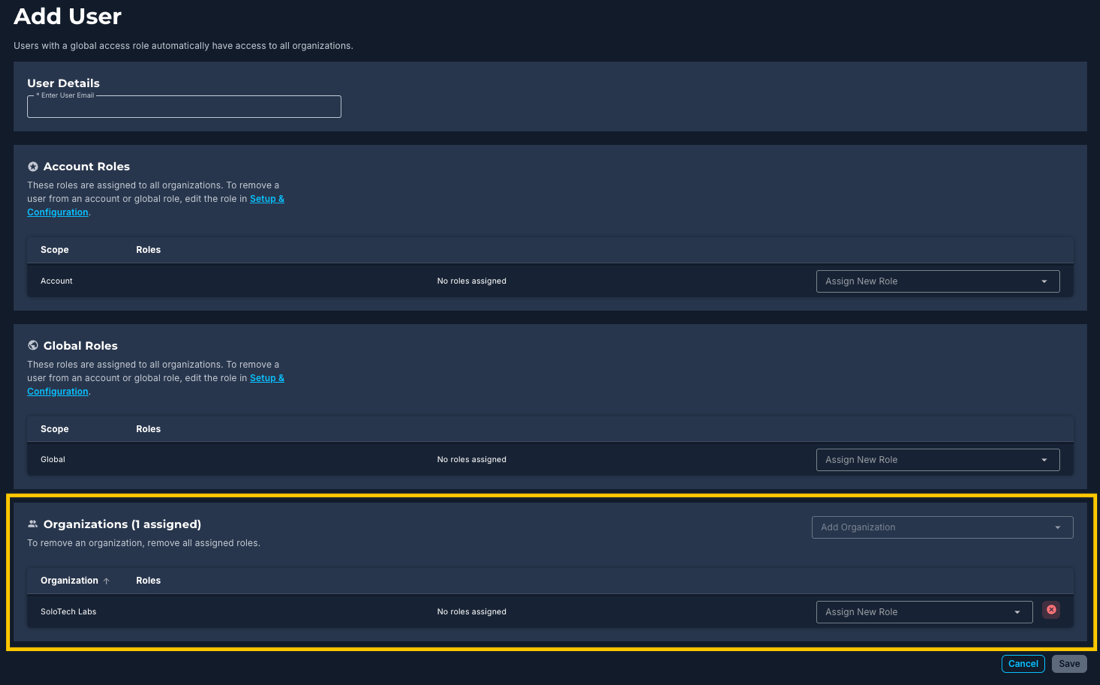
You can limit the permissions of any user to just one organization. There are two ways to configure this setting:
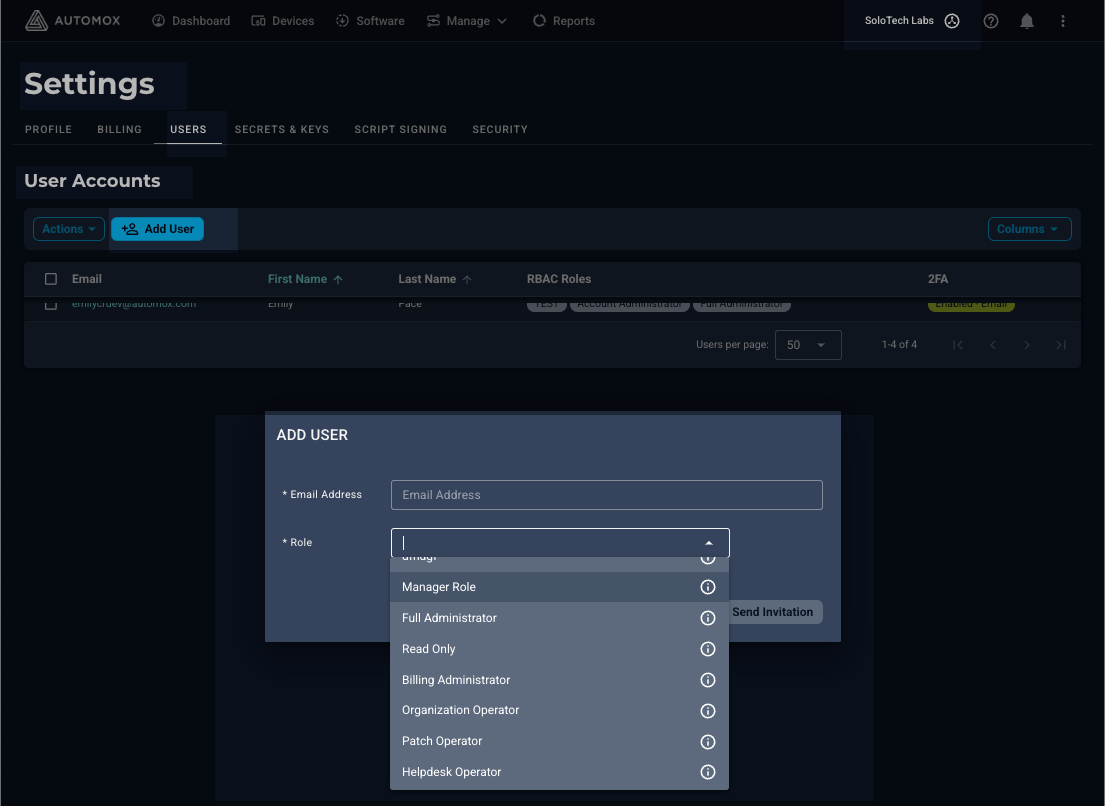
- From the Setup & Configuration > Users page (see previous image), select Add User and under Organizations select the organization and role you want the user to have access to. You can select more than one organization or role, as needed.
- You can also assign user roles from an organization’s Settings > Users page. Select Add User and select from the roles available. Any role selected here is only applicable to the specific organization.
Note: This is useful for an administrative user role that is limited to one organization. With the corresponding permissions to assign roles to other users, that administrator will be able to assign roles within the specific organization.
- If you do not want roles to be automatically inherited across all future organizations, ensure that roles are assigned at the organization level rather than global level.
Role Management Best Practices
To effectively manage role-based access control (RBAC) within a single organization, consider the following best practices:
Assess Access Needs
- Evaluate the access requirements of each role based on job functions.
- Identify necessary permissions to ensure employees can perform their responsibilities without excessive access.
Define Clear Roles Based on Job Functions
- Create roles that align with specific job responsibilities.
- Avoid unnecessary overlap between roles to maintain clarity in access control.
Apply the Least Privilege Principle
- Grant only the minimum necessary permissions required for a role to perform its duties.
- Reduce security risks by limiting unnecessary access.
Audit Access Regularly
- Conduct periodic reviews of role assignments and permissions.
- Ensure users have appropriate access levels as roles evolve within the organization.